On this article we will have a deep look at ISIS from the military point of view and so we will analyze their structure, materials, way of fight and different tactics and tricks used by them on the battlefield.
If you like it I would be grateful if you could share it.
Table of content:
- ISIS in the attack
- ISIS on the defense
- Terrain, positions and dynamics
- Antitank defenses
- IEDs and mines
- Antiair defense
- Evolution: The egg wants to be a condor
- The individuals
- VBIEDs
- Artillery
- Drones
- Snipers, sharpshooters and designated marksman
- Technicals and DIY vehicles
- Chemical warfare
- Deductions about their military organization
ISIS in the attack
Depending on the degree of surprise foreseen by ISIS planners they may employ different tactics to assault a position and they are not tactics so far from those used by a conventional army. Most times they do a dismounted assault with fire support from technicals and sometimes spearheaded by a tank at whose back the soldiers advance, this is a very primitive tactic but still useful against low quality forces like those from Iraq and Syria are in most cases.
Another times when there is a big plain between them and their enemies and especially against Kurdish backed by a powerful air force they advance fast and supresively, this time the VBIEDs will open the way while mechanized infantry units advance mounted in DIY armored vehicles moving at top speed against enemy positions and at the same time they open suppresive fire against the enemy positions, by doing this so fast they are provoking in the enemy a panic reaction that ultimately leads to give up the position because of the fear to be surpassed, essentially this is known as a mounted attack a very risky option from the point of view of a conventional army mainly compensated by its fastness.
When they are dismounted the assault tactics of the infantry are quite typical, the main part of the weaponry consists of assault rifles either from AK or M-16 series, also a few machine guns normally from PK series are used to provide suppresive fire, hand grenades are used before rush in the enemy position or to clean close spaces, finally RPG-7s are used against fortified positions like walls, barriers or wickets.

The use of technicals varies a lot between different forces but normally they comprise 14,5 and 23 mm guns while sometimes they can also mount 57 mm S-60 guns or M1939 37 mm guns or even recoilless rifles.
Tanks are used as mobile shields and the infantry advances from behind also they are used for heavy and direct fire support and just under some conditions they are able to engage enemy tanks, also it is very likely that normally because of the expensive and scarce ammunition for the main gun they just use coaxial or top mounted machine guns.

The use of tanks in urban warfare has appeared just a few times in ISIS videos but maybe this is an underrepresented way of use in ISIS media because they normally record big victories and urban warfare is a slow advance one and so it doesn’t provide the glorious image that ISIS wants to present on their videos, also it must be said that the most common antitank warheads are PG-7V and PG-7VM both capabe of penetrate every T-54, T-55, T-62, Type 59 or Type 69 in Iraq or Syria with the exception of the T-55(A)MV and so use them during urban engagements is a risky option.
By knowing their armor, the protection capability that it offers and the mainly offensive spirit of the tank they normally use them during their fast attacks in the open, with especial success against the Syrian Army and their allies during flanking maneuvers to cut their rearguard and always accompanied by motorized or mechanized infantry to assault and occupy positions.
Also about the how the attack is performed they normally attack a position from multiple axes and a whole area by attacking from various sides, especially exploiting weak points in the defensive system and trying to threat the main supply routes by doing a pincer maneuver and taking advantage of the fear to be surrounded of the defenders.
During the course of the operations ISIS must be 24/7 aware of the enemy air forces and so the deployment of advanced air observers to prevent as much as possible the incoming enemy air strikes is a likely option to be used, but to be fair the best ISIS way to deal with enemy air supremacy is the use of misleading tricks against the air observation.
It is very likely that normally they move in groups as small as possible because otherwise the probability of detection and engage by enemy jets is higher but if they move in groups of just two or three cars they can be considered possible civilians and so do not be attacked, but when ISIS suffers a heavy offensive and they need to move large reinforcements in a short period of time it is unavoidable to send large convoys, when doing so they expose themselves a lot but still it is very likely that they try to move during the night when in theory air supremacy is less effective.
For what I have been told normally Daesh basic combat unit is called “Fassil” and is equivalent to a motorized squadron, it usually consists of three SUVs Toyota, one of which would be responsible for the logistic functions, this type of unit would consist of about 10 men armed with assault rifles, one or two machine guns, one rocket launcher and some hand grenades, of course ISIS is not as homogeneizated as a professional army and so this structure is not omnipresent but still this may give us a clue on how they work.
The organic addition of one logistic SUV sounds like a guerrilla evolution created when they needed high autonomy and independence on the battlefield against the US, this kind of unit might be much more difficult to locate and decide to engage by an air force and also it reduces the logistics footprint for the Caliphate, while its disadvantages would be the difficulty to concentrate and coordinate large forces in brief periods of time, but it is true that the combat environment being faced by ISIS is relatively slow and numerically low in comparison with what a conventional army would expect what compensates the disadvantages at a certain degree.
Another typical trick even used by Iraq during 1991 consists in generate big columns of smoke by burning some crtitical places with very inflammable content, also against the link officers from artillery or the air force they also burn large amounts of tires to generate a smoke screen not as dense as when a big installation is burnt but still effective for a short period of time, this kind of tactics were heavily employed when the great operation to reconquer Mosul started.

Like the smoke Daesh tends to use the cover of sandstorms to launch large assaults and we have also seen some night raids by their best units. some of them even using silenced pistols.
Another common tactic used by ISIS is related to the use of large amounts of dummy vehicles simulating military ones, of course this is a very old trickc but it is still interesting to find it on ISIS hands. It is possible that at a certain degree the old Saddam’s officers are behind something like this because it corresponds to high intensity warfare not well known by guerrilla groups.

We also think that dummy vehicles are not massively used but just when they want to confuse enemy air survelliance and make them spend time and ammunition on false targets while the main operations are ongoing in other part.
It has been relatively common to see some strange large inventions consisting on a kind of big umbrella totally covering a tank, this could be used during the displacement phase to the concentration areas before being clearly detected or even during an offensive to protect them from the jets above by hidding the vehicle.
Most of these tricks are more effective against the SyAF whose airplanes most of the times are outdated and so their systems are not so capable to detect this kind of ruses.
Another common trick is related to the use of tunnels at every level, from the front to the homefront to move and store resources, to live in, to be protected from air strikes and artillery before an attack and to safely move troops from one point to another in to an area with prepared defenses, like a village or a town.
ISIS on the defense
Terrain, positions and dynamics
The predilect ISIS defense is established in a medium size urban area with some civilian population to be used as human shields, a big net of tunnels to comunicate different key points and a well knowledge of the surroundings to avoid the enemy to enter the town but if it happens they may have a few strongpoints well entrenched with a lot of IEDs deployed to resist.
Sometimes when they want to cover a retreat from a position they let a few suicides at their back and they get out during the night, also I have not confirm it but it is possible that sometimes they use light forces equipped with technicals and a few ATGMs to delay the enemy and screen the movements of the main force.
ISIS understands well that the objective is not to build positions with very gross walls but rather difficult to locate because once it is known it is just a matter of time that jets, helicopters or artillery will reduce it to ashes.
Oposite to the ISIS «doctrine» has been the finding of tanks being used as pillboxes on fixed positions covered at the top by the roof of a house, while we are not sure if it was because of the lack of fuel for their tanks in our opinion it just represents a desperate decision to use a valuable tank that otherwise would be absolutely useless.
Some elements normal for every army like dig trenches, put obstacles for the vehicles, clear the fields of fire, demolish buildings to cut roads, build barriers to avoid enemy to see them or even use blankets to cover certain areas or certain gaps on tunnels are also typical of Daesh.

Sometimes we have even seen them build something like petrol moats to act as fire barriers and above all again generate smoke against enemy observation both from ground and air.
The defense on open terrain is uncommon because it means huge disadvantages for them because of the lack of heavy armor, materials to build defensive lines in deepth, unexperience on that field, and exposure to enemy observation especially of the fixed positions.
We think that populated locations are their guide and reference to establish defensive positions and it is very likely from their point of view that every urban stronghold has the means to protect its position and at a certain degree its surroundings with its own material, while there must be something like «motorized reserves» by using technicals and civilian vehicles ready to be moved when one stronghold is attacked by a superior force, this may specially work in terms of ATGMs, a relatively expensive, scarce and vital weapon to defeat the core of the armored forces attacking them, however if the fight goes inside the town things would work different and evolve to something very close to an attrition battle.
While in our opinion there is not a clear way of defend by ISIS in terms of formations like a perimeter defense or a reverse slope or so in our opinion they tend to use a mix of them and specially prepare ambushes in some relatively open terrain inside the towns, in places like parks, parkings, or big buildings or complex of buildings with some open ground surrounding them.

Antitank defenses
ISIS antitank defense engagement ranges table

How does ISIS engage armored forces, and especially tanks?
If we think it cold, ISIS on the ground is facing an outmatching armor, in Iraq they fight against M1A1 Abrams and T-72Ms, in Syria they fight against T-90s, T-72Bs from advanced variants and other capable tanks, and against Turkey they are fighting against Leopard 2A4s and M-60Ts, try to battle them as equals by counterposing their own armored forces wasn’t a viable option for ISIS and so they have developed quite complex but not new antitank tactics.
The best long range AT weapon of ISIS is the ATGM, while they have operated a lot of ATGMs we can say that the 9M111 Fagot, 9M113 Konkurs and 9M133 Kornet are the most common among their forces, while missles like the Konkurs or the Kornet maybe are not able to deal at the front with the most advanced tanks like the M1A1 or the T-90 it is sure that every ISIS ATGM hitting the side will probably penetrate and cause big damage to even the most advanced tanks.

At medium ranges from approximately 1.200 or less metres the best ISIS weapon is the recoilless rifle, normally a 73 mm SPG-9 but also B-10s or M40s, very effective against modern tanks if they hit them on the sides but they need a certain degree of training to be fired, in exchange they are much cheaper than ATGMs and so they can also be used against lightly armroed vehicles and infantry.
Finally at close ranges like 400 metres or less they use RPGs, normally RPG-7s but sometimes M72 LAWs or similar one-shot bazookas, also for area denial or to canalize enemy forces they employ important amounts of minefields using both conventional or DIY mines, they also employ heavy weapons like 12,7, 14 and 23 mm calibers against lightly armored vehicles and hand grenades or even antitank grenades at very close range.

Another tactic used by ISIS to engage enemy armor consist in use large concentrations of mortar fire, that is a very common tactic among profesional armies but not so common in the case of non-state actors with small amounts of ammunition at their dispposal, it has not been widely documented but on the claimed page of 15 vehicles destroyed by ISIS in Syria two or one were because of likely or confirmed mortar fire, this gives us a percentage of 7,5% to 14% by comparison the ATGMs, the most effective weapon of the Caliphate represented slightly more than 50%. The problem is that some weapons are better suited to be recorded than others and mortars are not good for that purpose because you need more than one camera and they are not as predictable and spectacular so maybe they do not appear on ISIS propaganda.
While some may ask why for example mines/IEDs are not so effective in my opinion it has a big relation with a good training because sometimes apart from the most obvious avenues of approach like roads or lanes they are not very good at identify the enemy attack directions and also they don´t have massive amounts of this kind of weapons, something very important when you want to deny areas.
Since the begin of the SCW on 2011 the use of ATGMs by every side has been very basic, normally it was a group of a few men with the launcher and the missiles who sighted and attacked an enemy force, but since the begining of 2017 we have seen an increasing refinement on the ISIS way of use of ATGMs, especially against the Turkish armor in Al-Bab.
For example let’s imagine a normal situation near Al-Bab, a formation of 4 Turkish M-60Ts is facing ISIS, M-60T is impermeable to every ISIS weapon so they must be attacked from the sides, but this unit is formed covering a big arch and so if one ATGM is shot it is very likely that one of the tanks will be able to locate the place where it was fired and open fire, from this situation arises a new necessity for ISIS, that is to strike more than one vehicle at the same time, a tactic that also leads to a bigger capability to destroy enemy vehicles because they will not have as much time to react.
We have seen a few recent double and even triple simultaneous ATGM strikes against a single unit of armored vehicles, what is a big problem to deal. This kind of attacks at the same time from different positions indicate a relatively high level of train and coordination because it requires to have previously selected the positions for more than one ATGM launcher and an officer to coordinate the action or at least pre-establish a common plan.
And that is the other point, the experience show us that ISIS has been able to correctly guess the best firing points against enemy armor and also a flexible enough force to move the scarce resources when and where they are required.
Also sometimes they use tunnels to position themselves behind the armored forces and strike them from the back where they are very vulnerable.
IEDs and mines
Daesh gathered a lot of experience about IEDs during the years of the occupation when they were normally planted on the expected roads where the foreign convoys were going to pass. There were a few types of IEDs like those using an impact fuse or those remotely activated by a phone call, also when attacking civilians, another field where AQI accumulated extensive experience, the use of artifacts with timeserver was possible.
But IEDs are not just hidden bombs but also for example DIY hand grenades used to equip their infantry.

While the use of this kind of artifacts to ambush Iraqi or Syrian forces as it was done during the occupation has had a paper during the Caliphate operations it is true that the main objective has shifted in favor of some new roles.
Fist of all when ISIS retires from a location they let it filled with hundreds of hidden booby traps used to continually produce loses to its enemies and so slowly bleed them out, also they are being used as a delay tactic to slow the enemy advance by randomly, and a lot of times hastily putting them on the likely enemy avenues of approach.
Finally we find quite likely that they use them as a typical mean to strenght some positions by putting fields of IEDs in front of them or to canalize enemy attacks towards some pre-established kill zones.

Antiair defense
As Oryx has stated along some very interesting articles ISIS has try a lot of things to do some damage at the air forces that harass them, some of the quite desperate actions like use D-30 guns on AA role or mount captured air-air missiles on trucks to use them as AA platforms have been an obvious fail and they are just intern psychological medicine to show their population and troops that they have specific AA units dedicated to shoot down jets while their true effects are null.
However the ISIS inventory of AA weapons consist of 12,7 mm, 14,5 mm, 23 mm, 37 mm and 57 mm machine guns and guns along with some MANPADs and a few ZSU-23-4 Shilka AA vehicles.
All of those weapons are effective against low flying aircrafts, but specially against helicopters because the jets normally don`t fly so low, for example the AA machine guns may have ranges as much as 2,5 km, 57 mm guns well managed may have a range of about 4 km and MANPADs depending on the model 6 km approximately.

This kind of material just allows for a close point AA defense situating the armament around the objective to protect it, however if they want to give a certain AA cover to some units who are likely to receive helicopter attacks the use of MANPADs AA units mounted on highly flexible civilian vehicles is probably their best option, especially when considering how scarce those weapons are, also the distribution of a few men armed with MANPAD forming a triangle may let them cover bigger areas, but if this consists just in one MANPAD units without coordination with the other ones their efficency must be very low especially considering the very low fly and use of countermeasures by modern helicopters, what makes aircrafts even harder targets for the MANPADs.
While in theory mos of this material is probably near the front close to the expected areas to be attacked by enemy helicopters it is very likely that some important fixed objectives or even important persons of ISIS get a point AA defense protection against possible raids of the Western Special Forces who will normally employ helicopters to go at the back door of ISIS letting those helicopters relatively exposed to this kind of systems.
In the other hand while a ZSU-23-4 vehicle could be relatively effective at close range defense if it is not able to use its radar it is nothing else than a self-propelled ZSU-23-2 and as happens with heavier AA systems ISIS has not been able to operate those radars.
Since the very first moment was obvious for everyone that ISIS wasn’t going to be able to defeat an air force but below that it is true that they have been able to shoot down a few helicopters.

Evolution: The egg wants to be a condor
While the first archaic origins of ISIS are even before 2003 it was after the US invasion of Iraq when the group grew up, especially since Al-Zarqawi took its lead until he was killed on 2006, during that time Al Qaeda Iraq, as they were known, adopted extremely violent methods and at a certian degree the way of think of that epoch has influenced the current ISIS lack of diplomacy derived from their radical think and actions.
Around 2011 the organization was badly wounded so they decided to begin a new «policy» based on attack prisions to liberate religious extremists and recruit them fot the group, later they also took advantage of the Syrian Civil War that had started on 2011 it is possible that during the first moments they acted as a moderate group to get financial and material support something that worked for some time.
But during 2013 the group took off his mask and occupied Raqqa and a big part of East Syria by expulsing the rebels and the Kurdish and again using very violent methods, this provided them with a huge amount of material, territory and population, at this point the true Islamic Caliphate was bornt, but it wasn’t until the summer of 2014 when ISIS made use of their penetration among Iraqi sunnies to hugely defeat the Iraqi Army around Mosul, a victory that was related to the sunnie disenchantment with the sectarian shia politics from Baghdag and an excellent use of psychology during the battles by ISIS.
When the victory over Mosul was completed ISIS was in full expansion of its power, its territories and above all their army.
They sewed a new army in a brief period of time, while it was still based in light infantry and guerrilla material and philosophy they get huge amounts of APCs, IFVs artillery and tanks what lead to the creation of the first armored and mechanized units, birefly they captured the next heavy material:
- Artillery: D-30, M198, D-74, D-44, D-20 guns
- Tanks: Their core is comprised by T-54/55 and Type 69 (a Chinese copy of the last) while also a few T-62s and T-72s are part of their forces, they also captured M1A1 Abrams, M-60Ts and Leopard 2A4s but they decided to destroy them because of their complexity and other reasons.
- APC: BTR-80s, MT-LBs, M-113s, M117s, Humvees, MRAPs
- IFV: BMP-1s
Apart from that they also captured huge numbers of personal equipment, ammunitions and light weapons, including mortars, ATGMs and recoilless rifles.

This new DIY combined arms force comprised some conventional artillery, tanks, APCs, survelliance drones, guerrilla motorized infantry units using technicals… While for example a typical T-55 is an outdated tank with a relatively bad armor unable to resist most of the AT weapons on the battlefield they still offer protection against most of the weapons. For example the Kurdish weapons available to penetrate a T-55 would be just their RPGs, their few ATGMs and their recoilless rifles.
The low availability of those AT weapons and the lack of training and experience on their use led to easy ISIL victories by even using outdated tactics from WWII, also the combination of tanks as rams along with the technicals to provide fire support and the dismounted infantry to assault positions was a strong capable force for the Syrian standards.
At that time the violent ISIS methods provoked an international response that led to rearm the Iraqi army, send Western forces and suit a strong air coalition able to make a lot of damage to ISIS, from the military point of view the violent ISIS methods provided them with some advantages and disadvantages:
- Advantages: it gave them international fame and in terms of radical sunnism it means that they became the beacon for the yihadis around the world and their supporters, also when their enemies were not surrounded they tended to runaway in certain situations thanks to the psychological impact of the very violent ISIS actions spreaded by their excellent propaganda media and the local support of part of the population.
- Disadvantages: all of those advantages gave them fast victories but it also meant that when a force was completely surrounded or it was composed of non-arab or non-sunnie groups they tend to fight fiercely making ISIS advance much harder thanks to their pitiless diplomacy. Also their declarations and acts activated a strong international response that ultimately was vital to defeat ISIS, of course the main element was the air coalition leaded by USA that was able to provide tactical support to Kurdish and Iraqis on the ground and even do damage in the deep of ISIS structure. Also they even get some unnecessary enemies among radical sunnie groups with whom they could have get agreements.
When this final step happened the pressure from the air coalition but also from the SyAF and the RuAF forced them to adapt to a new kind of warfare where they were been continuously harassed from above and so the use of their new hardware was more difficult and required more caution decreasing its effectiveness forcing them to adopt new tricks and tactics.
When ISIS arrived to Syria it was an Iraqi group with around 2.000 fighters, but one year later they controlled a big part of Syria and Iraq with a few tens of thousands of troops and plenty of heavy material, while explain this growth is difficult we think that some reasons are related to the calling effect of their victories among local populations and a intelligent diplomacy towards yihadi groups both from outside and inside Syria and Iraq what ultimately allowed to the creation of a big army in a short period of time able to defend very distant fronts against multiple enemies.
The individuals
VBIEDs
The suicide bomb vehicles are used as a second artillery to produce a first shock before the main echelon assaults the position or as a ram against an entrenched force or a strong point, but the suicide drivers are a relatively expensive and limited weapon on hands of ISIS and so they are probably assigned to a unit depending on its mission and with a pre-stressed amount of VBIEDs at disposal giving the field commander a silver bullet to be used during the critical moments of the battle.
The experience of ISIS with VBIEDs was gathered during the insurgency against USA but those VBIEDs where relatively unpowerful and badly protected in comparison with the threat that we are facing now.
There is probably a certain high degree of centralization to on one hand recruit, brainwash and test suicide drivers and on the other hand design the vehicle to be used and the explosives to fill it.
A typical VBIED would be a chevy with a few hundred kilograms of payload from wich a part is deviated to add armored plates to the vehicle and so protect it from the weaponry that the enemies of ISIS are going to use desperately and in mass against it, this extra protection along with a relatively high speed (probably superior to 100 km/h) make these artifacts a big threat on the battlefield.


Artillery
Most units from ISIS have mortars and at a certain degree other types of DIY artillery with a low accuracy but with some level of effectiveness when used in mass.
Conventional artillery is not very common and normally it is just seen on the main offensives as a support force along with mortars, although the degree of ability to manage the artillery pieces may vary a lot between different units.
The artillery tends to be used in the same way as VBIEDs to produce a shock before the first assault or even to pound enemy positions especially to defeat some enemy resistance that may slow the main axis of advance or weak fortified positions. They have the problem that most of their pieces are not self-propelled and so they can’t follow the assaulting force at great distances because they are very exposed to enemy aircraft while being towed through the roads.
The best piece of the artillery parque of ISIS probably is the M198 155 mm US howitzer a very accurate gun able to provide a deadly firepower, but the most used piece is by far the Soviet designed D-30 light howitzer, a 122 mm gun relatively easy to manually operate and with a relative light weight perfect to be transported and even hidden from air coalition jets, also its low weight makes it suitable to be installed on platforms such as trucks meaning that ISIS has self-propelled artillery, however a civilian truck is not well suited for pieces like this and so their performance is relatively bad in comparison with military dedicated SPHs.


While conventional artillery is assigned to units depending on ther mission and are probably part of fully dedicated artillery units it is very likely that most of the ISIS units have at least an organic mortar support group or something close to it but still it is dubious the level of ammunition availability for this kind of weapons with high rates of ammunition expenditure.
The mortars mainly comprise they typical 81 and 120 mm calibers and as we have already told looks like every ISIS unit with certain size has its own support group based on mortars, a deadly weapon if its is well managed.
Drones
Apart from propaganda the main use of drones by ISIS has been to recognize the terrain before the offensive and probably to correct the artillery fire, so we have seen a lot of times how unarmed ISIS drones were shoot down, this is because they were doing survelliance missions a very useful tool for the ISIS military planners.
The appearance of ISIS armed drones is quite recent and as it could be consider by some as a mere psychological weapon in my opinion is just another weapon with a big psychological impact but also with some level of capacity to help ISIS wear out its enemies by its massive use and with an increasing level of menace, especially to unarmored vehicles transporting ammunition or uncovered infantry in the open.
We are not sure about their way of use but we think that it could be a mix of direct support assigned to a unit or also they act as lonely hunters looking for opportunity victims close to an area of operations limited by its autonomy.

What is sure is that they have been trained to choose their objectives because in our opinion they are looking for open roofs on the vehicles, this is becuase their main aerial bomb is based on a 40 mm grenade with a kill ratius of 5 metres and a very small penetration capacity, so the best way to use it consist on hit somewhere open with a lot of explosives on it, like Humvees but also tanks with the hatch open, a tactic that in spite of be quite homely has proved effective and at a low degree can be considered as another anti armor ISIS weapon.
Also it has some advantages like the low cost of civilian drones and the operators training, and also the cheap ammunition used of course if they face EW equipment they have no chance, but an even bigger force of drones might be the backbone of a low-cost terrorist air force that must not be underestimated.
Snipers, sharpshooters and designated marksmans
The use of snipers (or similar ones) by Iraqi insurgency groups is not new, when they were facing the West superior firepower most tactics shifted to hit & run because it denied the Western to make use of their superior firepower by calling air support and so between these hit and run tactics the sniper played an important role as it was able to do deadly shots from the distance and stay undiscovered.
Generally speaking some of the most common long range rifles on ISIS hands are the U.S M24 using a 7,62 x 51 mm cartridge, the Mosin Nagant using a 7,62 x 54 R cartridge and the king of the popularity, the mythical SVD Dragunov or its foreign copies.
As an idea of their potential the SVD series are accurate enough at around 700 to 800 metres on hands of experienced snipers and with a powerful scope magnification.

Snipers are assigned to the units more as sharpshooters than as snipers to support the forces during the attack or for attrition tactics along with IEDs or so inside urban environments.
A very typical combo is the usage of snipers along with IEDs in abandoned towns, for example when ISIS forces left Sinjar to the Kurdish they let it filled with booby traps and a few snipers to produce some more casualities to their enemies a very efficient cost/effective way to deny the complete control of some area to the enemy and make him divert some sources to it.
Also it must be said that the camouflage knowledge of the main part of the ISIS snipers is quite basic being reduced to some mimicry, also a lot of times they act as anti light armor by using high caliber sniper rifles like the Sayyad-2 able to penetrate Humvees, M117s, M-113s and other light armored vehicles.
Technicals & DIY vehicles
Technicals or as we can call them «gunneds» essentially are civilian SUVs or trucks with a weapon mounted at its back for direct fire support, normally those weapons have no plating and they usually mount the next weapons:
- MMGs and assault rifles: sometimes on some vehicles they add firing ports to let the troops inside open fire with its light weaponry, a good improvement while doing mounted attacks.
- HMGs: DShKM 12,7 mm, and KPV, ZPU-2 or ZPU-4 of 14,5 mm
- AA guns: ZU-23-2 double automatic gun of 23 mm, 57 mm S-60 guns on trucks and sometimes even 37 mm M1939 guns or their Chinese copies.
- Recoilless rifles: this is not a common upgrade but when it exists normally uses a U.S M40 of 105 mm mounted on a jeep, this upgrade means a lot because it is thought to be used as a tank hunter by fastly moving to a position an effective tactic against badly trained tank crews.
But sometimes they directly design absolutely new and huge vehicles that I call gunned castles which add a lot of bulletproof plates and a few levels with HMGs mounted on them what creates very strange combinations that remind us to some WWI vehicles. Their objective is to safely transport as much fighters as possible while at the same time those vehicles provide a great suppressive fire in all directions, something vital during frontal attacks on a plain.

In the end we can say that gunneds are the IFVs of the poor and because they are put on good platforms like civilian Toyota pick ups they have a good mobility, a good cross country ability, a low logistic footprint and a high reliability, something vital in combat situations.
Chemical warfare
From all of the abilities deployed by ISIS on the battlefield the more complex at the moment by far is the use of chemical weapons in limited amounts, while we are not sure if it has been done by trained fighters or by a grave recklessness this is a worrisome issue.
While the use of chemical agents by ISIS has been limited unfortunatelty we can not say that it has been anecdotic nor ineffective.
Most likely all agents came from captured Syrian and Iraq installations where those weapons were already produced and storaged.
But chemical weapons have several things to be known and considered before use them, like direction and speed of the wind, humidity, concentrations needed of the agent to both incapacitate or kill, the use of the precursor substances from the binary system and the dispersion vehicle/weapon to be used what is not an easy ability for an originally guerrilla group.
The ability of ISIS to produce operative chemical weapons is very unlikely so their capacity on this field is closely related to the amount of ready to use ammunitions captured in Syria and Iraq and the level of availability of the dispersion vehicles.
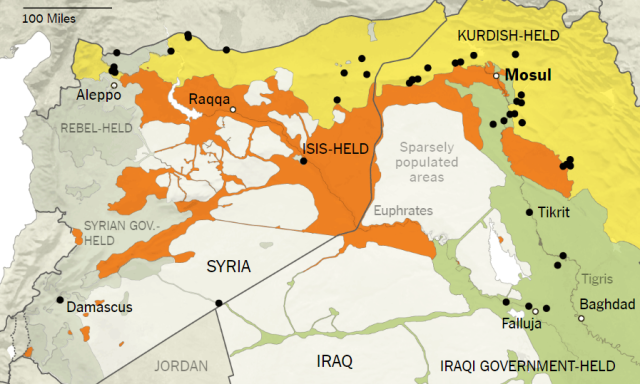
If we take a look at IHS map where 52 confirmed chemical attacks by ISIS have been documented we can see that most of them have taken place against Kurdish both from Iraq and Syria, in our opinion this could be related to a correct ISIS think about the lower readiness of Kurdish against this kind of weapons especially because in theory they haven’t get NBC equipment and training so they are very exposed to gases. Also the use of the agents tends to be more psychological than tactical.
At the moment the degree of mortality reached suggests the use of some common chemical agents like the sarin, the chlorine or the mustard gas, the three present in the Syrian inventory, but fortunately none of those is one of the «top tier» gases of the Syrian government which are the tabun and the VX. From those agents on hands of ISIS the sarin is by far the most powerful.
Training
Of couse the different weapons of ISIS may require different trainings but above all a light infantry training is probably the one that ISIS has been mainly providing, this comprises the use of assault rifles, machine guns, hand grenades, RPGs, basics about movements, fire and maneuver, camouflage, orientation, close combat, basic field fortifications…
Some normal units probably get a specialized training about ATGMs, artillery, snipers, MANPADs, mortars, recoilless rifles and in certain occasions about armored vehicles.
A big part of ISIS comprising experienced yihadis do not need training and also a big part of the local militias supporting them are badly equiped and not very trustable so they probably don’t receive a good preparation.
Finally the core of their recently erected force comes from people and volunteers recruited inside and outside the Caliphate, then they are probably classified, most of them have no military experience but a few may have done the military service or even have served in Syrian or Iraqi army and so they could have very valuable experience as mechanized infantry, light infantry or tanks, if so they may receive new specific training and been sent to those especial units.
It is very likely that most of the light infantry training and especially that locally recruited is trained at its own Wilayat to take advantage of their known of the terrain, society and climate, but this arises the question about their training standards.
We have seen how pupils from ISIS held territory get some ISIS-edited books, so if it has happen at the educational level it is very likely that it has also happened at the military level and so they have produce their own brief and adaptative military manuals for the training camps and their instructors.

Unfortunately we don’t have much information about ISIS training and especially about their local recruiting system, their training philosophy or the duration of the instruction phase.
Deductions about their military organization
The main civilian administrative unit of ISIS is the governorate (Wilayat) with a governor and his subordinates and advisors.
The growth of ISIS was too large and too fast, especially in the case of Syria where they were not as present as in Iraq before 2013, their fast evolution adding groups of globalist yihadis, Chechens, Iraqis and Syrians in both scenaries with huge fronts comprising deserts and towns, desertic and mediterranean climate, and been facing very different threats including Iraqi Kurdish, Syrian Kurdish, rebels from Syria, Turkish supported forces, SAA, Iranian militias etc could not have been done without a great level of decentralization, but the problem arrives when we try to decide what is the true level of military decentralization.
Let’s take the defense of Al-Bab as an example, was it just a defense organized by the corresponding Wilayat or there was a declared theatre of operations charged to one commander independent from the Wilayat? In our opinion the tactical defense in normal situations is mainly responsability of a Wilayat and its commander by providing most of the resources needed to successfully accomplish the mision, while there must be a certain degree of coordination with the Central HQ to apply for new resources and some big strategic or operational operations are prepared by the Central HQ that sends specific elite units and commanders to the area.

There could be a high level of central control over some especial units like tanks, conventional artillery, suicides, drones, highly experienced fighters from outside or MANPADs to be provided at critical moments. At first look we may think that with the increasing pressure of air supremacy the movements may have get more difficult and so the move of fighters and material from the Central HQs in Mosul or Raqqa at distant places is very risky, but this is probably mitigated by placing the bases and training camps near the most likely operational theatres, by this way the Central HQ just would need to give the orders and the especial units would be relatively close to their destinations and so the possibility of been caught by enemy aircraft largely decreases.
Also it is very likely that apart from the political orders and some basic military instructions the autonomy about planning and acting in the battlefield is very high and especially in everything referred to warfare material, for example the Chechens units probably retain a certain degree of autonomy in the battlefield and they buy or get their own weapons from loot, black market or ISIS arsenals at their will.
Finally ISIS presents us a very monolithic and solid image but would be interesting to know how the hierarchy works among different human military groups like Chechens, tribes, Syrians or Iraqis because the existance of so much differences among those groups that sometimes are even lobbies inside ISIS can make the Caliphate much splitted than we actually think.
I would like to especially thanks to Historico for his excellent article about the use of tanks by ISIS and also to Purple Olvie for his excellent work about ISIS VBIEDs and to Oryx for his nice cover of some ISIS battles in its blog.
You can help me to do more articles by donating me some money via paypal here.
If you want to contact me for questions or to write an article for you, you can contact me on minstertipo@gmail.com orat my Twitter account @MinsterTX.



A good prognosis of the fighting doctrine of the ISIS. What I thought lacking is the calibre of the officers and also the methods of instilling discipline, are drugs used by their foot soldiers?
Me gustaMe gusta
That is an interesting question that deserves an article on its own, however I can tell you that it is thought that at least in an important number of cases their troops consume drugs.
Me gustaLe gusta a 1 persona
Pingback: A deep look at the heart of ISIS war machine: From tactics to doctrine – Thinking Syria